Automation maturity model
This module helps business leaders to assess their organisation’s automation maturity. This ensures the adoption of automation technologies is strategic, efficient, and effective.
Determine your automation maturity level
To successfully scale a self-sufficient automation model, your organisation’s executives must champion the strategic vision. Leadership drives cultural transformation, technology excellence, metrics and KPIs, and governance structures. Assessing your organisation’s maturity level is crucial to guide it toward the desired strategic automation maturity level.
The automation maturity model (AMM) below will assist organisations in understanding and identifying automation maturity levels.13,30,31,32 It will support you in determining the desired future state and the suitable operation model implementation to reach it.
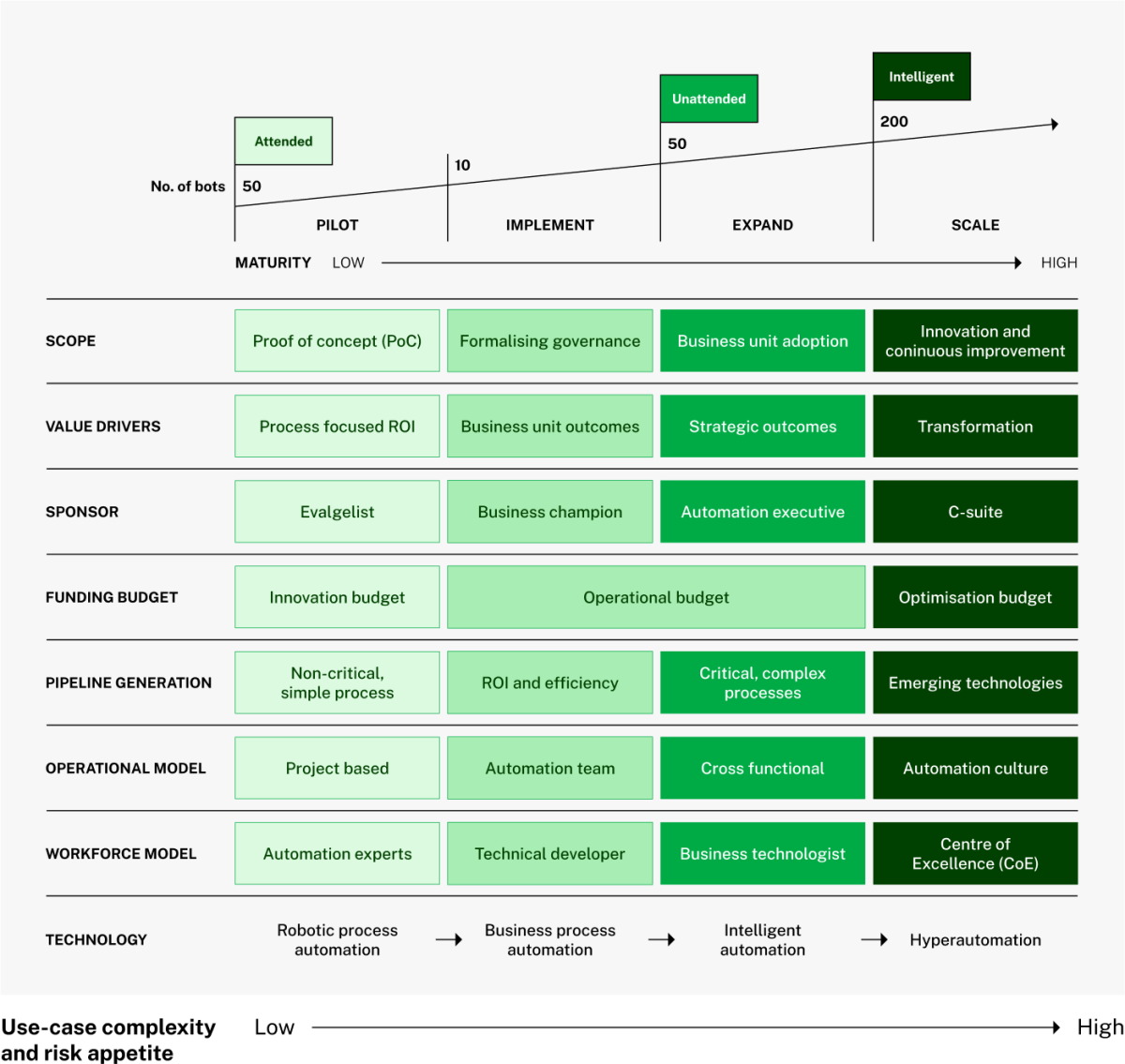
The automation maturity model above leads to hyperautomation, a transformational and mature level of automation. Hyperautomation is an evolving and transformational business-driven automation strategy.31,32 In hyperautomation, any business operation that can be automated, should be. The hyperautomation concept effectively integrates different types of automation technology supported by process reengineering and real-time data optimisation.
To achieve hyperautomation, leaders must align automation with organisational goals. This includes fostering a culture of innovation, proactive change management, and investment in employee capability to achieve self-sufficiency. Assessing organisational pillars such as strategy, risk, culture, and operations can help measure the organisation’s maturity phase.
Pilot
The pilot level is the ideal time for your organisation to explore and test automation opportunities because risk is low. Organisational leaders allocate limited resources to develop proof of concept (PoC) projects and build an appetite for automation within your organisation. In the low-risk context of the pilot phase, leaders capture insights on the feasibility of automation and viable technology.
Discover the characteristics of the pilot level in the accordion below.
| Definition | Initial phase of implementing automation solutions. Small-scale, controlled experiments are conducted to assess the feasibility, benefits, and challenges of automation. An automation sponsor in your organisation is identified. |
|---|---|
| Key characteristics |
|
| Focus |
|
| Scope |
|
| Value drivers |
|
| Sponsor |
|
| Investment model |
|
| Pipeline generation |
|
| Operation model |
|
| Workforce model |
|
| Automation bots |
|
*Bot number ranges vary based on organisation context.
| KPI | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| PoC success rate | Measure initial automation PoCs success against objectives. | Indicates automation potential and feasibility in your organisation. |
| Time and cost savings | Assess savings of automation as compared to manual processes. | Indicates benefits of automation in your organisation. |
| Employee feedback and Adoption | Gather feedback from employees involved in pilot. | Measure employee acceptance, appetite and proficiency with the proposed automation. |
| Error reduction rate | Catalogue error reduction after process automation. | Measures discrepancies to prove value of processes automation. |
Implement
At the implement level, your organisation integrates identified automation initiatives into strategy planning, defining goals and metrics. As the return on investment (ROI) and cultural acceptance of automation increase, your organisation’s risk tolerance and willingness to invest in further automation use-cases will grow. This will create a context where dedicated automation teams and formalised governance structures can develop to implement future projects.
During automation implementation, leadership’s focus should shift towards:
- Optimising efficiencies
- Deploying automation more broadly across a department or agency.
- Building a data-driven, automation culture that emphasises process KPIs such as efficiency, error reduction and cost savings.
- Employees up skill programs
- Change management.
Discover the characteristics of the implement level in the table below.
| Definition | The implement level indicates your organisation has progressed from the pilot phase and is formalising its automation approach. Implementation may involve setting up a dedicated Centre of Excellence (CoE) automation team. |
|---|---|
| Key characteristics |
|
| Focus |
|
| Scope |
|
| Value drivers |
|
| Sponsor |
|
| Investment model |
|
| Pipeline generation |
|
| Operation model |
|
| Workforce model |
|
| Automation bots* |
|
*Bot number ranges vary based on organisation context.
| KPI | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Process automation rate | Measure the process automation rate. | Indicates organisation’s progress in implementing automation. |
| Training effectiveness | Assess the efficacy of automation employee training programs. | Enhanced adoption and utilisation of automation technology. |
| Operational efficiency | Evaluate automation’s improvement to operational efficiency. | Indicates your organisation’s increased productivity. |
| Cost per transaction | Calculate the cost per transaction for both manual and automated processes. | A decrease in this metric indicates cost savings. |
Expand
Expansion involves integrating automation across areas in your agency. To expand automation across your organisation, leaders break down silos, adopt a mindset of continuous improvement and an automation-first culture. They prioritise cross-functional collaboration and automated process interoperability.
Successful automation projects are scaled during expansion, and high-impact initiatives receive investment. Processes continue to be standardised and optimised to increase efficiency. Key success indicators include integration efficiency and cross-functional collaboration metrics.
Discover the characteristics of the expansion level in the table below.
| Definition | Entering the expand level signifies the organisation's intent to extend the reach and impact of automation initiatives. It involves scaling automation adoption across various business functions and units and using unattended automation. |
|---|---|
| Key characteristics |
|
| Focus |
|
| Scope |
|
| Value drivers |
|
| Sponsor |
|
| Investment model |
|
| Pipeline generation |
|
| Operation model |
|
| Workforce model |
|
| Automation bots* |
|
*Bot number ranges vary based on organisation context.
| KPI | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-functional integration | Measure the success of integrating automated processes across different business functions or areas. | Indicates an organisation's ability to break down silos and cross-functional collaboration. |
| Adoption across business units | Assess the adoption of automation across various business units. | Demonstrates successfully cultivating a culture that prioritises automation. |
| Feedback efficacy | Evaluate the efficiency of feedback between users and the automation team. | A streamlined feedback process facilitates continuous improvement and innovation. |
| Scalability assessment | Evaluate solutions capacity in handling changed workload. | Ensures implemented solutions can scale to handle increased workloads. |
Scale
During scale, your organisation fosters an Agile, innovation, and automation-driven culture derived from strategy-led, enterprise-wide transformation. Also, during scale, organisations have higher risk tolerance, mature automation operations, can manage complexities, and drive continuous improvement. Achieving scale indicates that your organisation has matured to operate a self-sufficient automation ecosystem.
Your organisation’s leaders must now focus on scalability, responsivity, and organisational Agility metrics. Investment in advanced technologies, bottom-up proactive identification of automation opportunities by employees, and ongoing employee upskilling are key characteristics of a mature automation strategy.
Discover the characteristics of the scale level in the accordion below.
| Definition | The scale level represents the highest level of automation maturity within an organisation. It involves the widespread deployment of automation across the enterprise, impacting core business operations and strategies. |
|---|---|
| Key characteristics |
|
| Focus |
|
| Scope |
|
| Value drivers |
|
| Sponsor |
|
| Investment model |
|
| Pipeline generation |
|
| Operation model |
|
| Workforce model |
|
| Automation bots* |
|
*Bot number ranges vary based on organisational context.
| KPI | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise-wide automation coverage | Measure cross-functional automation adoption. | Indicates organisation’s success in scaling automation across departments. |
| Time to implement new initiatives | Evaluate the organisation speed of implementing new automation initiatives. | A shorter time indicates efficiency in scaling. |
| Business impact KPIs | Track KPIs such as increased revenue, enhanced customer and employee satisfaction. | Demonstrate an organisation’s holistic benefits of scaled automation. |
| Employee upskilling and retention | Assess the success of upskilling programs and monitor employee retention rates. | Indicates the agility and ability of organisation to adapt its workforce to automation. |
Next to explore
Skills and capabilities
This module details the organisational characteristics required to build a successful, sustainable and scalable automation transformation roadmap.